Pharmaceutical dosage forms can be classified into liquids, gases, solids, and semi-solids depending on the form. Most drugs are developed for oral administration of a solid dosage form. Among them, powders, granules, capsules, and tablets are common solid dosage forms.
Powders
A powder is a dry powdered preparation prepared by pulverizing and uniformly mixing a drug and a suitable auxiliary material. This medicine is available for internal or external use.
The general process of powder preparation includes pretreatment of materials, pulverization, sieving, mixing, sub-dosing, quality inspection, packaging and storage, etc.
The focus of packaging and storage of powders is on moisture. Because of the large dispersion of the powder, its hygroscopicity and weathering are significant.
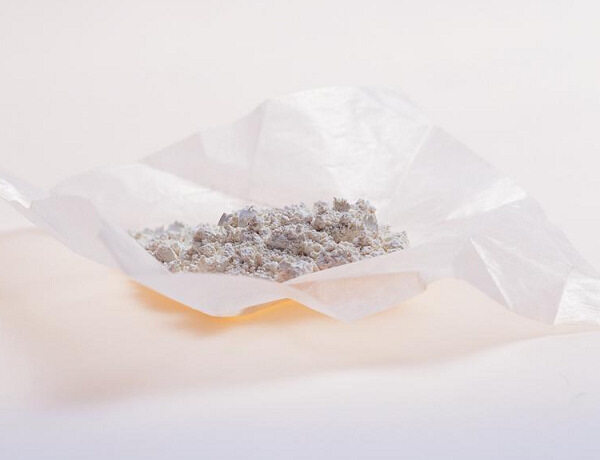

Features:
1. The powder has a large degree of pulverization, a large surface area, so it is easy to disperse and has a fast effect;
2. When used externally, the powder covers a large area, which can simultaneously play the role of protection and convergence;
3. It is convenient to store, transport and carry;
4. The preparation process is simple, the dosage is easy to control, and it is convenient for infants and young children to take.
Granule
Granule refers to a dry granular preparation having a certain particle size prepared from a drug and a suitable adjuvant. Its uniformity should be noticed when storaging granules. This medicine should be sealed and stored in a dry place to prevent moisture deterioration.
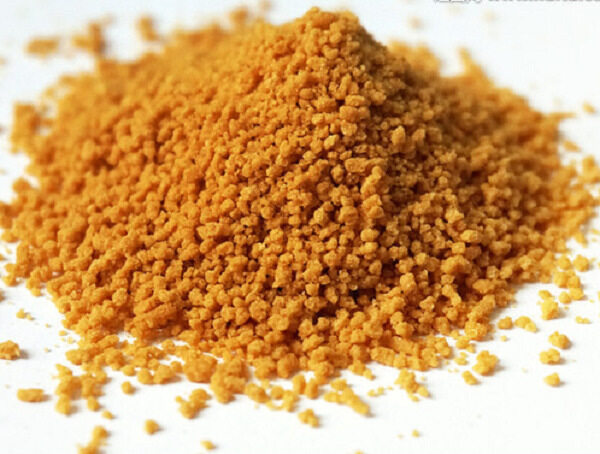

Features:
1. The dosage is small, and it is convenient to take, carry, store and transport.
2. Granules dissolve and release quickly, and have high absorption and utilization rate, which can effectively prevent discoloration, lamination and the like which occur during tablet production.
3. Granules are suitable for industrial production, and the product quality is stable.
4. If necessary, it can be coated or made into a sustained release, enteric preparation.
Capsule
Capsules include hard capsules and soft capsules. A hard capsule refers to a solid preparation prepared by filling a drug in a hollow hard capsule or sealing it in an elastic soft capsule.
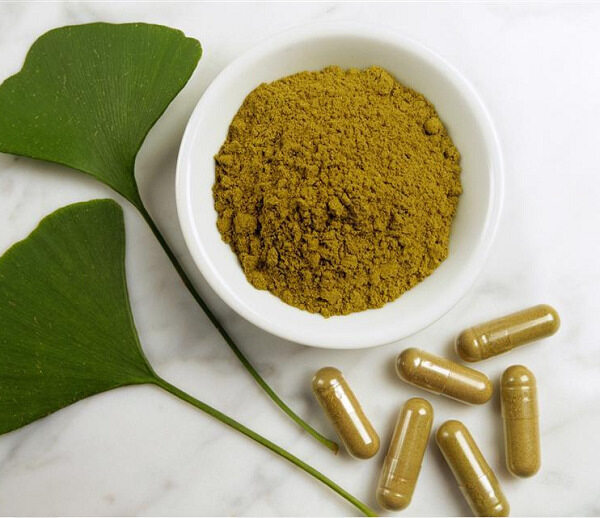

Features:
1. It can mask the bad smell of drugs and improve the stability of drugs.
2. The drug in the capsule is directly filled in the capsule in the state of powder or granules, and is not affected by factors such as pressure, so the drug can be rapidly dispersed, dissolved and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Its bioavailability will be higher than that of pills, tablets and the like.
3. Capsules can make up for the deficiency of other solid dosage forms. For example, drugs with high oil content or liquid drugs are difficult to be made into pills, tablets, etc., but can be made into soft capsules.
4. It can delay the release of drugs, achieving the purpose of positioning release.
Tablet
A tablet refers to a solid preparation of a wafer or an anisotropic sheet which is prepared by a formulation technique after the drug is uniformly mixed with a suitable auxiliary material.
Features:
1. The dose is accurate and the content is uniform;
2. The medicinal stability of the drug in the tablet is better because it is small and dense, and is less affected by external air, light, moisture and other factors, and is also protected by coating when necessary;
3. It is convenient to carry, transport and take;
4. The mechanization and automation of production are high, therefore the output is large;
5. Tablets have a variety of different types, such as compressed tablets, sugar-coated tablets, enteric-coated tablets, film-coated tablets, chewable tablets and buccal tablets to meet the needs of different clinical medical treatment.


